-

How Much it ll cost to build an app like
- Cost to develop an Uber Tow Truck App
- Cost to develop a Pest Control App
- Cost To Develop a Handyman App Like Uber
- Cost To Develop a Doctor Appointment Booking App
- Cost To Develop An App Like MoodBites
- Cost To Develop An App Like SkipTheDishes
- Cost To Develop An App Like Q Chat
- Cost To Develop An App Like TickTick
- Cost To Develop An App Like ContractBook
- Cost To Develop An App Like Utter
-

How Much it ll cost to build an app like
- Cost to develop a Video Editing Mobile App like Magisto
- Cost to develop a Live Video Streaming App like Twitch
- Cost to develop an app like Home Workout- No equipment
- Cost to develop a Sports News app like theScore
- Cost to develop an Application like Reddit
- Cost to develop a Sports News app like theScore
- Cost to develop an E-learning platform like Udemy
- Cost to develop an On Demand Doctor App like Heal App

UI/UX Principle 4: Scrolling is faster & easier than Paging
Websites today use more vertical real property.
The pages are longer than ever. But in the past, websites were designed with everything “above” the fold. We believe the fold should not be viewed as a line.
Although rich content is attractive above the fold, users will still be drawn to the experience by the speed and efficiency of scrolling through pages and scanning them – not clicking and waiting for content to appear.
“Scrolling Beats Paginating” – It’s faster and easier
Jakob Nielsen pulled the old standard guideline, which forbade the creation of pages that required users to scroll in 1997.
He said that scrolling beats panning because it is faster to scroll than wait for pages to load. This boils down to the simple fact that a single long page is more beneficial than multiple pages shorter, which require a click and a wait time to access.
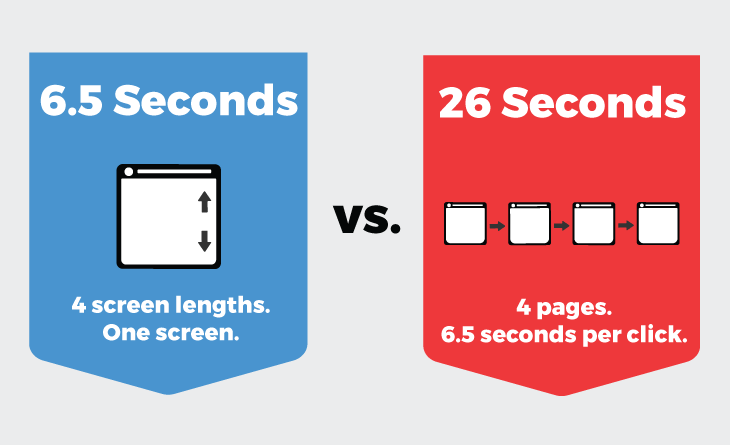
This is consistent with research that people scan websites instead of reading them. Web page refreshes can slow us down. We scan pages very quickly but take an average of 6.5 seconds. Ask yourself: “What would our users rather do?” You can navigate to 4 pages in 26 seconds, or scan a longer homepage quickly without needing to wait for several page refreshes.
This is a straightforward question that has a simple answer. Our tolerance for scrolling has increased, as well as our propensity to scroll on mobile and tablet devices. When designing web experiences, we must consider this user behaviour.
Therefore, long web pages are now common
These are three examples from the Awwwards group, which recognizes and rewards great websites.

Vertical real estate is often used to tell stories on award-winning websites. This is not only the case for award-winning sites. The graph below shows that the largest companies in the world have long pages.
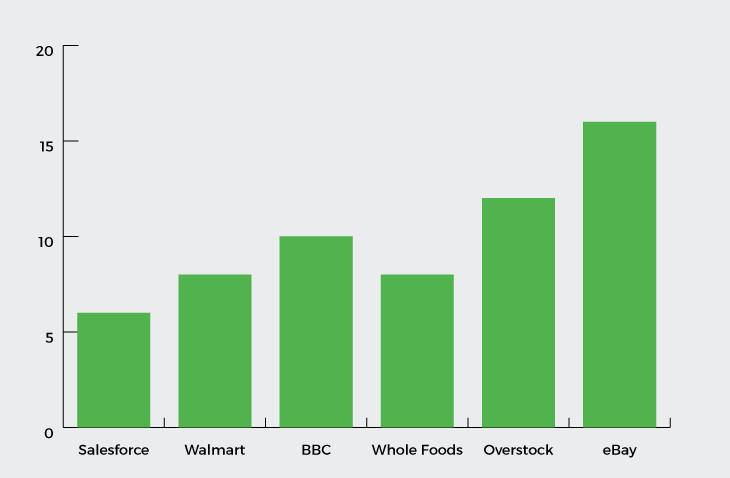
Amazon has done a lot of research on usability and the Kindle page they have is quite long. However, it works. Amazon’s unique approach to e-commerce is not the best, but it shows how pages are becoming longer. This is a sign that designers should consider this.
Additional Reading about Page Lengths and Navigation
Flat navigation, which is closely related to the discussion about tabs, consolidates pages and makes full use of the vertical real property. It reduces the number of layers used for navigation. Flat navigation also adapts to modern web users’ behaviour and how they search for information. Flat navigation is a more efficient way to navigate the web and it also makes it easier for users to use. It is also closely related to scrolling.
Conclusion
Modern business websites show a growing trend towards longer pages that provide a more engaging experience. It’s becoming less important to add more pages, and instead, ask users to connect the dots. Although this may seem like a fad to some, it is a growing trend that shows scrolling will be a more common user behaviour in the future.

Author
Our Partners




WhatsApp us


